Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood that starts in the bone marrow and spreads to the bloodstream. It is more common in adults, but each year approximately 500 new cases of AML are diagnosed in children in the United States.
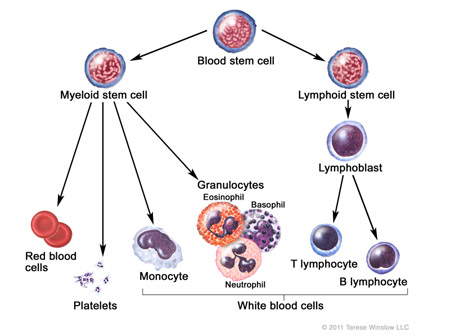
Leukemia begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue located inside the bones, where blood cells are made. Leukemia starts when a single, young white blood cell, called a "blast" develops a series of mistakes or mutations that allow it to multiply uncontrollably. Eventually, the blasts accumulate and crowd out normal cells in the bone marrow. They can also spill out into the bloodstream, and invade the lymph nodes, brain, skin, liver, kidney, ovaries, testes, and other organs. Occasionally they form a solid tumor called a "chloroma."
Last updated September, 2011
Newly Diagnosed with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
In Treatment for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
After Treatment for Acute Myeloid Leukemia








